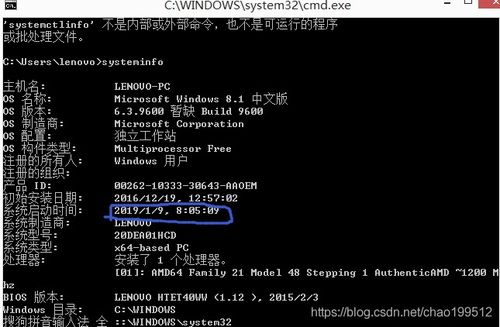
windows获取系统启动以来的时间,使用系统API获取启动时间
在Windows操作系统中,获取系统启动以来的时间是一个常见的需求。无论是为了系统监控、性能分析还是其他应用场景,了解系统自启动以来的运行时间都是非常有用的。本文将详细介绍如何在Windows平台上获取系统启动以来的时间,并提供相应的代码示例。
使用系统API获取启动时间
1. 使用NtQuerySystemInformation
通过调用NTDLL.DLL中的NtQuerySystemInformation函数,可以获取系统的详细信息,包括启动时间。以下是该函数的原型:
NTSTATUS NtQuerySystemInformation(
IN UINT SystemInformationClass,
OUT PVOID SystemInformation,
IN ULONG SystemInformationLength,
OUT PULONG ReturnLength OPTIONAL
要获取系统启动时间,需要将SystemInformationClass参数设置为SystemTimeInformation(值为3),然后解析返回的SYSTEMTIMEINFORMATION结构中的liKeBootTime成员即可。
2. 使用GetTickCount
GetTickCount函数返回自系统启动以来经过的毫秒数。这是一个非常简单且常用的方法,适用于不需要高精度时间的情况。以下是该函数的原型:
DWORD GetTickCount(void);
该函数返回的值是一个无符号整数,表示自系统启动以来经过的毫秒数。
3. 使用KeQueryTickCount
在Windows驱动开发中,可以使用KeQueryTickCount函数获取系统启动以来的滴答数。该函数返回的值是一个长整型,表示自系统启动以来经过的滴答数。以下是该函数的原型:
VOID KeQueryTickCount(
OUT PLARGEINTEGER TickCount
需要注意的是,滴答数在不同硬件环境中可能不同,因此在使用时需要结合KeQueryTimeIncrement函数获取滴答数增量。
代码示例
以下是一个使用NtQuerySystemInformation函数获取系统启动时间的Rust代码示例:
extern crate winapi;
use winapi::ntdll::NtQuerySystemInformation;
use winapi::ntdll::SystemTimeInformation;
use winapi::ntdll::SYSTEMTIMEINFORMATION;
use winapi::ntdll::LARGE_INTEGER;
fn main() {
let mut system_info = [0u8; 1024];
let result = unsafe {
NtQuerySystemInformation(
3, // SystemTimeInformation
system_info.as_mut_ptr(),
system_info.len() as u32,
std::ptr::null_mut(),
)
};
if result == 0 {
let boot_time = (system_info.as_ptr() as const LARGE_INTEGER);
println!(
